14 The HELIOS Service Controller
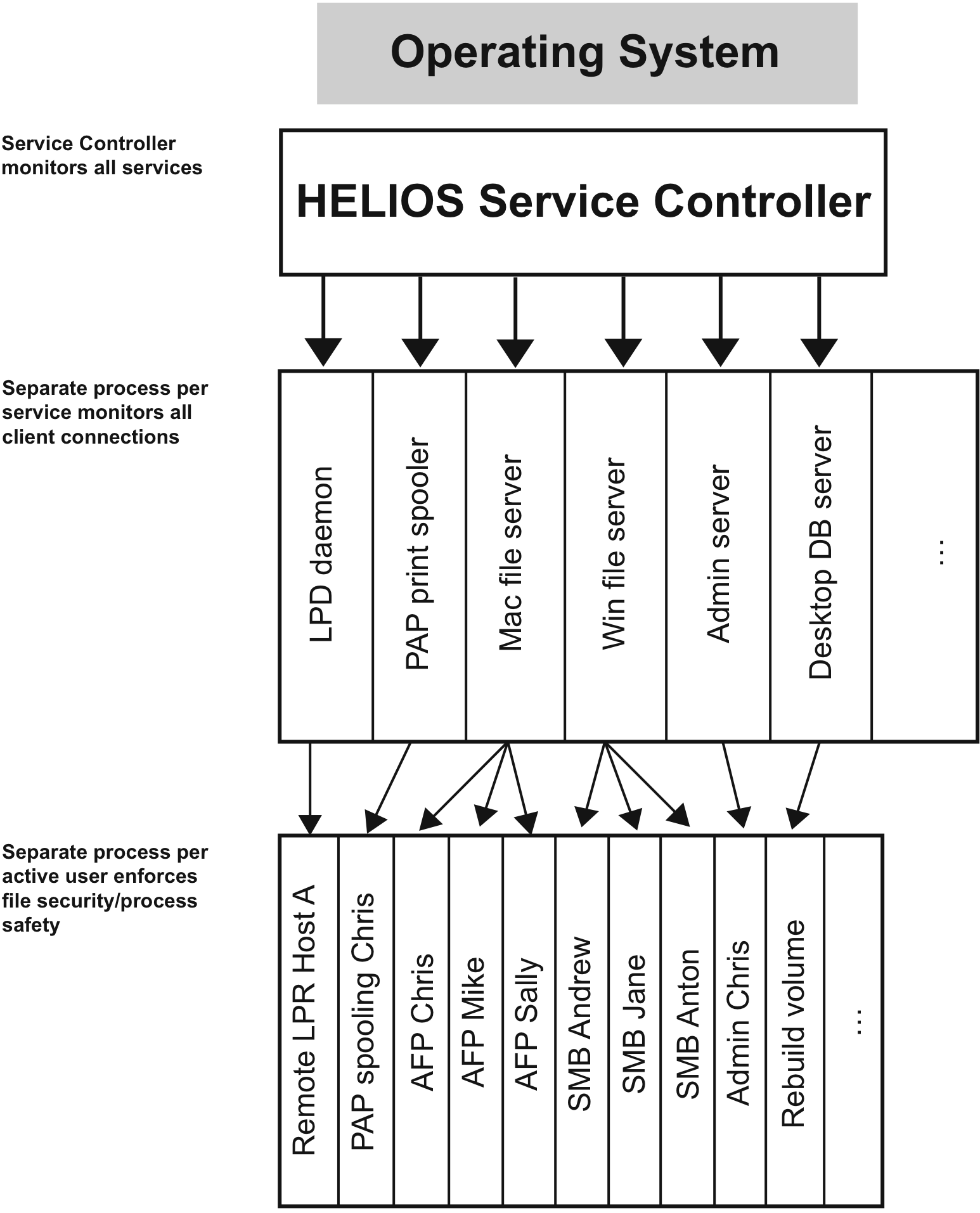
The HELIOS Service Controller “srvsrv” is a feature, which starts, stops and monitors all HELIOS server processes, like “afpsrv”, “pcshare”, “lpd”, etc. (the figure on the next page shows HELIOS’ three levels of service reliability).
This feature prevents a possible server process failure for a single client from bringing down all the served clients on the network. By having a separate process for each client computer, each user is effectively insulated from other users. The more users on the network, the more important this feature.
The HELIOS Service Controller monitors all processes which have been started on the server. In case a process should fail, the HELIOS Service Controller restarts this process after a short time.
Automatic service restart 10 seconds after failure
Automatic disable after 10 failures; each failure within a minute
Automatic starting order of the services, e.g.:
afpsrv first
opisrv second
…
Automatic stopping order
Complete error logging into “syslog” file
Third party applications can integrate their services into the HELIOS Service Controller (via preferences; see also 14.2 “Integrating additional services”)
14.1 srvutil
“srvutil” is a server utility which lets you manipulate single HELIOS services, e.g. starting, stopping, reconfiguring or just status monitoring. Actually, it passes requests to the “srvsrv ” daemon which is described above.
The following options can be used with the “srvutil”
command, where [-f] means forced
and [-r] recursive:
srvutil start all (root only) srvutil start [-r] [-f] service... (root only) srvutil stop all (root only) srvutil stop [-r] [-f] service... (root only) srvutil reconf all (root only) srvutil reconf service... (root only) srvutil status (all users)
- start -f
Starts service though depending services might not yet run
- start -r
Starts service and all other depending services
- stop -f
Stops service though depending services might still run
- stop -r
Stops service and all other depending services
- Note:
-
The
srvutil stopcommand can additionally be used with the[-g]option, which stops the service in a specified time period (in minutes), optionally with a shutdown message[-m]. Both options only have effect on “afpsrv” and “pcshare” services, other services such as “lpd”, “admsrv”, etc. will ignore them and stop immediately.
- Example:
# cd /usr/local/helios # bin/srvutil stop -f pcshare -g 1 -m "PCShare stopped."
This command stops the PCShare service (“pcshare”) after a grace time of one minute and with the message “PCShare stopped”, though “opisrv”, which depends on “pcshare”, is still running.
- reconf [all]
Causes a master process to reread its configuration file or preferences
- status
Shows the status of all installed (HELIOS) services
14.2 Integrating additional services
The HELIOS Service Controller can also be used to start and stop additional server processes.
If you want to integrate additional services into the HELIOS software, which are administered by the HELIOS Service Controller, do the following:
-
Generate a text file containing the preference(s) for a new service and save it under a suitable name, e.g. “myservice.prefs”.
A simple example for a service preference file is: “HELIOSDIR/etc/prefs/lpd.prefs”.
- Example:
“myservice.prefs”
[][Services][myservice][ExecPath] flags=0 type=String value=[14] sbin/myservice [][Services][myservice][DependsOn] flags=0 type=Stringlist value=[4] [6]atalkd [7]desksrv [6]afpsrv [7]pcshare
The above example defines a service executable “sbin/myservice” that must be started after “atalkd”, “desksrv”, “afpsrv”, and “pcshare”.
-
Install the preferences for the new service via:
# prefrestore myservice.prefs
For more information on the “prefrestore” command see also 8.15 “prefrestore”.
The new service is started with the next “start-helios” command.
The preferences for the HELIOS Service Controller are listed in 19.4 “Service Controller preference keys”.