HELIOS Base UB+ User manual |
||||
16 mDNS (Bonjour)
16.1 Introduction
Bonjour, also known as zero configuration networking, enables automatic discovery of computers, devices, and services on IP networks. Bonjour uses industry standard IP protocols to allow devices to automatically discover each other without the need to enter IP addresses or configure DNS servers. The HELIOS mDNS (multicast DNS) server implementation is based on the Apple Bonjour server. To provide a true zero configuration experience, Bonjour requires that devices implement three essential parts:
HELIOS mDNS fully implements part II and III. The automatic IP address configuration of the HELIOS server is up to the operating system and networking environment. HELIOS mDNS uses the existing IP configuration.
mDNS uses IP UDP network packets to exchange information. mDNS is a joint effort by participants of the "IETF Zero Configuration Networking" (http://www.zeroconf.org) and "DNS Extensions" (http://ietf.org/html.charters/dnsext-charter.html) working groups.
16.2 mDNS vs. AppleTalk
A good starting point is a simple comparison between mDNS and AppleTalk. Historically, AppleTalk handled zero configuration very well and is still being used. The goal of mDNS is to offer similar services based on standard IP networks.
A standard AppleTalk entity registration looks like:
lw8500:LaserWriter@HELIOS Support"lw8500" represents the device name, "LaserWriter" the type, and "HELIOS Support" the AppleTalk zone.
A standard mDNS registration looks like:
lw8500_printer._tcp. local. 515 pdl=application/postscript
16.3 Host names with DNS and mDNS
Computer host names are usually resolved by use of a local "hosts" file lookup table, or when configured from a DNS server. Some DHCP servers, e.g. PCShare's built-in DHCP server, can automatically update a DNS server with the preferred computer name. Applications and system utilities, e.g. the "ping" command will resolve host names into an IP address.
Applications must use the mDNS client APIs to resolve mDNS registered host names, e.g. the host name "macbook.local" to the corresponding IP address. The HELIOS "mdnstool" allows mapping the name into an IP address, e.g. mdnstool -Q "macbook.local".
Apple's host resolving will automatically resolve host names via both DNS and mDNS.
When Apple's Bonjour installer package (not the HELIOS mDNS installation!) is installed on Windows, an included Apple Bonjour NameSpace Provider (mdnsNSP) will resolve host names via both DNS and mDNS.
The deployment of mDNS in a local network needs zero configuration to find its services. In this case all host names are in the "local" mDNS domain, e.g. ping macbook.local. For wide area network names the existing DNS servers must be updated manually to handle the name resolving.
Apple Bonjour adds capabilities ("Wide Area Bonjour") to register its names with an existing DNS server. This requires additional configuration and a trusted DNS server. At present, the HELIOS mDNS server does not support "Wide Area Bonjour".
16.4 Coexistence of Apple Bonjour and the HELIOS mDNS server
On Mac OS X, HELIOS services will not include the HELIOS mDNS server. The existing Apple mDNS server "mDNSResponder" is used instead. All HELIOS services and tools are compatible with the existing Apple Bonjour server.
On Windows, the HELIOS mDNS server will check whether the Apple Bonjour Server for Windows is running and, if yes, use it. If the Bonjour Server is not running the HELIOS mDNS server will be used instead. If HELIOS services are installed on Windows it is recommended to use the HELIOS mDNS server because support is provided via HELIOS and its partners.
16.5 HELIOS mDNS server
The HELIOS mDNS server implements the multicast DNS protocol which is called "Bonjour" by Apple. The HELIOS mDNS server supports all network interfaces with a valid IPv4 network interface. All IPv4 activated network interfaces are detected by default and used by the HELIOS mDNS server, which is part of the HELIOS Base product. Basically, no configuration is needed.
The HELIOS mDNS server is called "mdnssrv" and it is started by the HELIOS Service Controller (see 14 "The Service Controller").
The default mDNS server name is adapted from the server's host name. If a different name is required the "mdnssrv" preference hostname (see 19.8 "mDNS server preference keys") allows specifying a custom host name used for mDNS.
The HELIOS network interface tool "ifstat" (see 8.8 "ifstat") lists all available network interfaces with their names, e.g.:
The mDNS service often uses the interface index to reference an interface name. Therefore "ifstat" can be used to find out configured interfaces and their index. If only specific interfaces should be used by the HELIOS mDNS server, the interfaces preference (see 19.8 "mDNS server preference keys") allows limiting the interfaces being used.
If a setting of the HELIOS mDNS server is changed the service must be restarted, to adopt the new settings:
srvutil stop -f mdnssrvsrvutil start mdnssrvAn automatic reconfiguration of the HELIOS mDNS server is not implemented because server environments are expected to be some more static and should not change automatically compared with mobile computers where an automatic configuration change is a great feature.
The HELIOS mDNS server uses the (UDP) IP port 5353, the mDNS Windows (TCP) IP port is 5354 (loopback only!).
mDNS local library communication requires the following resources:
Registration types used by HELIOS:
16.6 Sample network configurations
Single server network with clients:
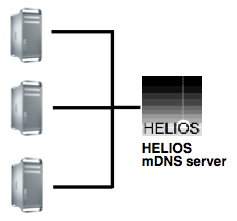
Single server network with two IP network interfaces:
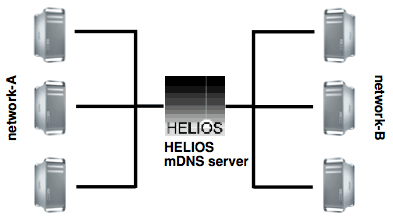 A client in network-A will see all mDNS names in network-A and network-B because the mDNS server will answer queries on both network interfaces.
A client in network-A will see all mDNS names in network-A and network-B because the mDNS server will answer queries on both network interfaces.
A client in network-A will not see names in network-B because the default IP multicasts are not forwarded by routers.
16.7 mDNS proxy server
The HELIOS mDNS proxy server ("mdnsproxysrv") forwards requests between network interfaces, and so allows connecting devices on different subnets, which would otherwise not "see" each other. HELIOS mDNS proxy also allows
- mapping mDNS host names to remote IP addresses
- registering non-Bonjour devices (printers, websites, etc.)
- easy mDNS registrations for third-party applications via the mDNS telnet service port
- synchronizing static registrations from primary server via the mDNS remote server port
16.8 Additional information
16.8.1 Automatic mDNS service reconnect
All HELIOS applications will automatically reconnect and re-register their mDNS services if an mDNS server should abort. The reconnect will be done every 10 seconds within the first minute, and later on every minute until the mDNS server is available again. This works also if the Apple Bonjour server is used.
16.8.2 Tracing the mDNS server communication
Network tracers like "WireShark" can decode the mDNS protocol.
16.9 mdnstool
HELIOS "mdnstool" is a network diagnostic tool, which allows browsing for registrations and registering names. It resembles Apple's Mac OS X "dns-sd" ("Bonjour") tool and can be used on all HELIOS supported platforms. Most of its functionality is not implemented in the binary itself, but in library code that is available to any application.
mdnstool [-E][-F][-B <Type> <Domain>]
[-L <Name> <Type> <Domain>]
[-R <Name> <Type> <Domain> <Port>][<TXT>...]
[-P <Name> <Type> <Domain> <Port> <Host> <IP>][<TXT>...]
[-C][-t][-H][-h]The following options can be used with "mdnstool":
Enumerate recommended registration domains
Enumerate recommended browsing domains
Browse for service instances
To find a list of all services use the type "_services._dns-sd._udp"Get the IP address of an mDNS hostname
Browse with port and IP address
Register a host record for an unknown host
May be arbitrary Unicode text (UTF-8), containing any legal unicode characters (including dots, spaces, slashes, colons, etc. without restriction), up to 63 bytes long.
Form: "_app-proto._tcp" or "_app-proto._udp", where "app-proto" is a registered application protocol name.
Domain in which to register the service. In current implementations, only the local multicast domain "local" is supported.
Number from 0 to 65535. The TCP or UDP port number upon which the service is listening.
Host name of the mDNS client, e.g. macbook.local.
IP address that the HELIOS mDNS server delivers upon request.
These additional parameters must be - if specified - the first argument:
(No auto rename of duplicate registrations)
In combination with registering a service, duplicate names will not be renamed into a number suffix. Instead an error will be reported.(Loopback interface only)
By default registrations and lookups are performed using all configured network interfaces. The -lo or -p option allows limiting the operation on a specified interface only.
Alternatively, you may specify the interface number using the -p option, e.g. -p4 (no space between option and number!).mdnstool -R testreg _printer._tcp local. 515Register the printer "testreg" on the standard "lpd" port (515) to the local Bonjour/mDNS domain. This registration is valid until the connection to the server is closed.
mdnstool -B _services._dns-sd._udpmdnstool -B -t2 _printer._tcpList all printers found while stopping the browsing after 2 seconds.
Timestamp
Time when service was last refreshed.A/R
Add or remove services. During a short request, there are probably only "add" messages. However, if running the tool for a longer time, when services disappear, also "remove" messages will be shown.Flags
Internally used flag field with the content:kDNSServiceFlagsAdd = 2 A service has been added.kDNSServiceFlagsMoreComing = 1 Additional messages in
the same packet.3 means a combination of both flags.
if
Internally used ID of the interface via which a message came in.Domain
Always local for mDNS messages; on DNS queries this might also be any other domain, e.g. helios.de.Service Type
Type description of the reported service.mdnstool -L testreg _printer._tcpGet more information on the printer "testreg" like the complete service name, its host and TXT resources.
mdnstool -Q <servername>.localGet the IP address of a local host.
Timestamp
See Browsing.A/R
See Browsing.Flags
See Browsing.if
See Browsing.Name
See Instance Name in Browsing.T
Actual type and class. A query does not just request service messages but internal server data. Service types as well as the classes are listed in the library file "libmdns.h".kDNSServiceType_A = 1kDNSServiceClass_IN = 1Rdata
Data received as a result of the query, e.g. the IP address of the queried server name.
| © 2008 HELIOS Software GmbH |